0x00 Introduction
how2heap 是一个堆利用技术系列教程,我会将这个教程的学习过程记录下来。
0x01 Overview
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "This file doesn't demonstrate an attack, but shows the nature of glibc's allocator.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "glibc uses a first-fit algorithm to select a free chunk.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "If a chunk is free and large enough, malloc will select this chunk.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This can be exploited in a use-after-free situation.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating 2 buffers. They can be large, don't have to be fastbin.\n");
char* a = malloc(512);
char* b = malloc(256);
char* c;
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(512): %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(256): %p\n", b);
fprintf(stderr, "we could continue mallocing here...\n");
fprintf(stderr, "now let's put a string at a that we can read later \"this is A!\"\n");
strcpy(a, "this is A!");
fprintf(stderr, "first allocation %p points to %s\n", a, a);
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the first one...\n");
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "We don't need to free anything again. As long as we allocate less than 512, it will end up at %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "So, let's allocate 500 bytes\n");
c = malloc(500);
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(500): %p\n", c);
fprintf(stderr, "And put a different string here, \"this is C!\"\n");
strcpy(c, "this is C!");
fprintf(stderr, "3rd allocation %p points to %s\n", c, c);
fprintf(stderr, "first allocation %p points to %s\n", a, a);
fprintf(stderr, "If we reuse the first allocation, it now holds the data from the third allocation.");
}
0x02 First-fit behavior
这个程序并不展示攻击,而是描述 glibc 的 ‘first-fit’ 分配行为。任何时候任何 chunk(除了 fast chunk)被释放后,会被放入 unsortd bin,将其插入链表的头部。当请求新的 chunk 时(除了 fast chunk),对 unsorted bin 进行初始化操作,从尾部开始遍历整个链表。遍历时并不进行精确检查,如果当前 chunk 的大小大于等于请求的大小,则将其分割成两块并返回,确保先进先出的行为。
看一下这部分代码:
char *a = malloc(300); // 0x***010
char *b = malloc(250); // 0x***150
free(a);
a = malloc(250); // 0x***010
unsorted bin 的变化为:
- 释放 ‘a’。
head -> a -> tail
- ‘malloc’ 请求。
head -> a2 -> tail [ ‘a1’ 被返回了 ]
因为请求的大小 (250字节) 小于之前释放的 chunk 大小 (300),所以 chunk ‘a’ 被分割成 ‘a1’ 和 ‘a2’,这跟 _int_malloc 函数的第6步 [iii] 对应。
fast chunk 的情况也是如此。不过释放后不是放入 unsorted bin,而是放入 fastbin 中。就跟之前提到的一样,fastbin 存储了一个插入和删除都是在头部的单链表,反转了 chunk 获取后的顺序。
请查看如下代码:
char *a = malloc(20); // 0xe4b010
char *b = malloc(20); // 0xe4b030
char *c = malloc(20); // 0xe4b050
char *d = malloc(20); // 0xe4b070
free(a);
free(b);
free(c);
free(d);
a = malloc(20); // 0xe4b070
b = malloc(20); // 0xe4b050
c = malloc(20); // 0xe4b030
d = malloc(20); // 0xe4b010
fastbin 的变化:
- ‘a’ freed.
head -> a -> tail
- ‘b’ freed.
head -> b -> a -> tail
- ‘c’ freed.
head -> c -> b -> a -> tail
- ‘d’ freed.
head -> d -> c -> b -> a -> tail
- ‘malloc’ request.
head -> c -> b -> a -> tail [ ‘d’ is returned ]
- ‘malloc’ request.
head -> b -> a -> tail [ ‘c’ is returned ]
- ‘malloc’ request.
head -> a -> tail [ ‘b’ is returned ]
- ‘malloc’ request.
head -> tail [ ‘a’ is returned ]
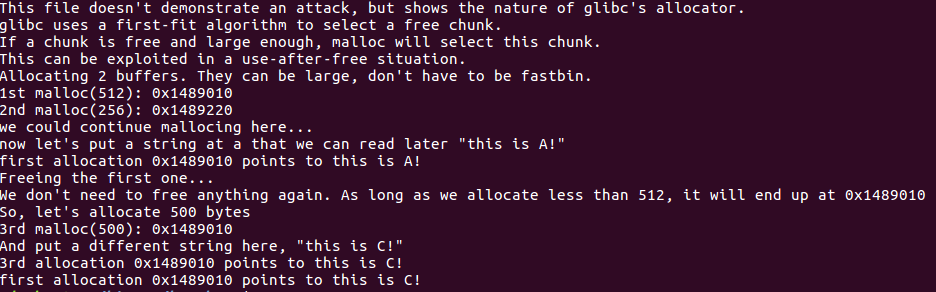
first_fit 运行截图:
至于 Use after Free 可以参考 https://sploitfun.wordpress.com/2015/06/16/use-after-free/